Energy-efficient windows are an excellent way to make your home more comfortable, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective. They help reduce energy consumption, decrease your carbon footprint, and save money on your energy bills. In this article, we will discuss what energy-efficient windows are, their benefits, and how they work.
What are energy-efficient windows?
Energy-efficient windows are windows that have been designed to reduce the amount of energy lost through them. They are made of materials that are insulating and reflective, and they use advanced glazing techniques to minimize the transfer of heat and light. Some of the most common materials used in energy-efficient windows include Low-E glass, argon gas, and vinyl or fiberglass frames.
Benefits of energy-efficient windows
There are several benefits to installing energy-efficient windows in your home. The most significant benefits include:
- Energy savings: Energy-efficient windows can save you money on your energy bills by reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool your home.
- Improved comfort: Energy-efficient windows can help regulate the temperature inside your home, making it more comfortable to live in.
- Environmental benefits: Energy-efficient windows can help reduce your carbon footprint by reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool your home.
- Increased home value: Energy-efficient windows can add value to your home, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
How do energy-efficient windows work?
Energy-efficient windows work by minimizing the amount of heat and light that is transferred through them. This is done through a combination of materials and techniques that help to reduce the amount of energy lost through the windows. Here are some of the ways that energy-efficient windows work:
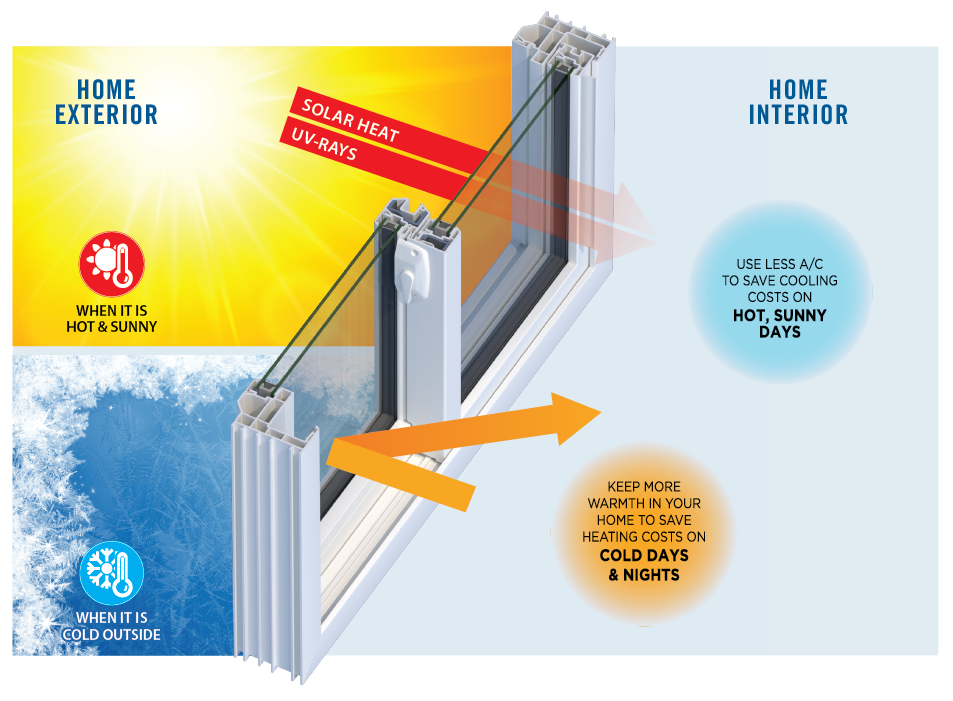
- Low-E glass: Low-E glass is a type of glass that has a special coating that reflects heat and light. This helps to keep the heat inside your home in the winter and outside in the summer.
- Argon gas: Argon gas is an inert gas that is used to fill the space between the panes of a double-paned window. This helps to reduce heat transfer and improve the insulating properties of the window.
- Vinyl or fiberglass frames: Vinyl or fiberglass frames are excellent insulators and can help reduce energy transfer through the frame of the window.
- Multiple panes: Double-paned or triple-paned windows have multiple layers of glass, which help to reduce heat transfer.
- Window coatings: Some energy-efficient windows have additional coatings, such as tinting or reflective coatings, that help to further reduce heat transfer.
Choosing the right energy-efficient windows
When choosing energy-efficient windows, there are several factors to consider. These include:
- U-factor: The U-factor measures how much heat is lost through the window. The lower the U-factor, the more energy-efficient the window.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): The SHGC measures how much solar heat is transmitted through the window. The lower the SHGC, the less solar heat is transmitted through the window.
- Air leakage: The air leakage rating measures how much air can pass through the window. The lower the air leakage rating, the more energy-efficient the window.
- Frame material: The frame material can have a significant impact on the energy efficiency of the window. Vinyl or fiberglass frames are excellent insulators, while aluminum frames are not as energy-efficient.
In conclusion, energy-efficient windows are an excellent way to reduce your energy consumption, decrease your carbon footprint, and save money on your energy bills. They work by minimizing the amount of heat and light that is transferred through them, using a combination of materials and techniques. When choosing energy-efficient windows, it’s essential to consider factors like U-factor, SHGC, air leakage, and frame material to ensure you get the most energy-efficient windows possible.

